backtest_ml has too long a run time
-
@illustrious-felice please help me @support @Vyacheslav_B
-
@illustrious-felice Hello.
I do not see any issues with the specified parameters. Please note that
retrain_interval_after_submit=1is set; after
submission to the competition, the model will retrain every day. If you plan to submit your strategy to the competition,
it is better to rewrite it for a single-pass mode. A quick quality assessment can be made using
precheck here.There are not many options for acceleration:
- Simplifying the machine learning model.
- Use local development here with a
powerful PC or run the script on a powerful server. - Reducing the amount of data fed into the model.
- Shortening the testing period for quick elimination of unsuccessful models. For example, you can look at the
financial results the model shows for the last year or another period.
You can also do some tricks with the input data, but there is a big risk of feeding future data into the model. If
technical indicators are fed into the model, they can be calculated in advance, but internally exclude the data of
already pre-calculated indicators.Here is an example of using a pre-calculated EMA
g_ema = qnta.ema(data_all.sel(field="high"), 15)import xarray as xr import qnt.backtester as qnbt import qnt.data as qndata import numpy as np import logging import qnt.stats as qns import qnt.graph as qngraph import qnt.ta as qnta data_all = qndata.stocks.load_ndx_data(min_date="2023-01-01", assets=["NAS:AMZN"]) g_ema = qnta.ema(data_all.sel(field="high"), 15) def load_data(period): return qndata.stocks.load_ndx_data(tail=period, assets=["NAS:AMZN"]) def predict_weights(market_data): def get_ml_model(): # you can use any machine learning model here from sklearn.linear_model import RidgeClassifier model = RidgeClassifier(random_state=18) return model def get_features(data): time_start = data.time.values[0] time_end = data.time.values[-1] ema = g_ema.sel(time=slice(time_start, time_end)) for_result = ema.to_pandas() return for_result def get_target_classes(data): # define categorical targets price_current = data.sel(field="close").dropna("time") # rm NaN price_future = price_current.shift(time=-1).dropna("time") class_positive = 1 class_negative = 0 target_is_price_up = xr.where(price_future > price_current, class_positive, class_negative) return target_is_price_up.to_pandas() data = market_data.copy(True) asset_name_all = data.coords["asset"].values features_all_df = get_features(data) target_all_df = get_target_classes(data) predict_weights_next_day_df = data.sel(field="close").isel(time=-1).to_pandas() for asset_name in asset_name_all: target_for_learn_df = target_all_df[asset_name] feature_for_learn_df = features_all_df[asset_name][:-1] # last value reserved for prediction # align features and targets target_for_learn_df, feature_for_learn_df = target_for_learn_df.align(feature_for_learn_df, axis=0, join="inner") model = get_ml_model() try: model.fit(feature_for_learn_df.values.reshape(-1, 1), target_for_learn_df) feature_for_predict_df = features_all_df[asset_name][-1:] predict = model.predict(feature_for_predict_df.values.reshape(-1, 1)) predict_weights_next_day_df[asset_name] = predict except: logging.exception("model failed") # if there is exception, return zero values return xr.zeros_like(data.isel(field=0, time=0)) return predict_weights_next_day_df.to_xarray() weights = qnbt.backtest( competition_type="stocks_nasdaq100", load_data=load_data, lookback_period=18, start_date="2024-01-01", strategy=predict_weights, analyze=True, build_plots=True )A different approach can be taken to develop algorithmic solutions based on machine learning. Initially, one can search
for strong machine learning models that show good accuracy, then test them usingbacktest_mlto discard weak models
beforebacktest_ml. -
@vyacheslav_b Thank you so much
-
@vyacheslav_b Thank you. Please help me with the issue RuntimeError: expand(torch.DoubleTensor{[694, 6]}, size=[694]): the number of sizes provided (1) must be greater or equal to the number of dimensions in the tensor (2).
I have tried adding the following feature:

However I got an error
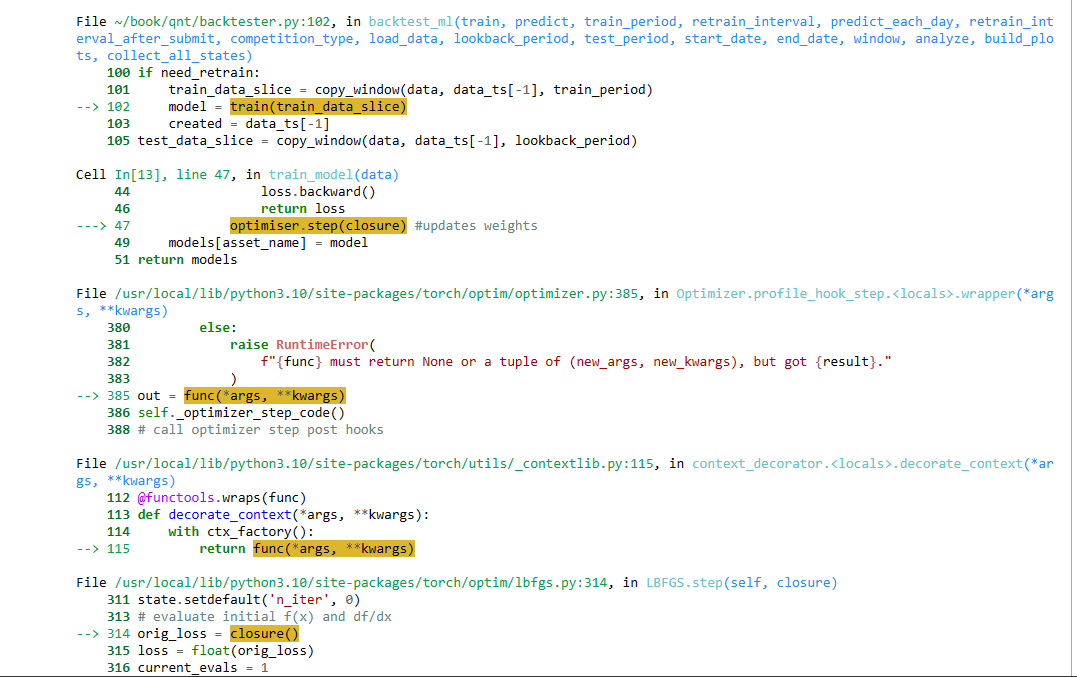
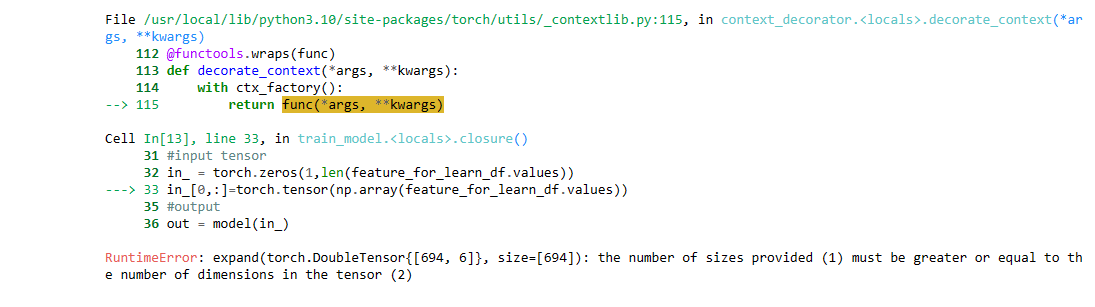
Please help me fix the error. I really need to fix this bug so I can train more than 1 feature. Thank you very much. -
@vyacheslav_b Hopefully you can give me a code example of LSTM when using more than 1 feature to train in the get_feaures() function and using more than 3 assets (stock codes). Thank you. Currently I am getting an error when changing the number of features and assets. Thank you so much.
I hope you can show me an example of changing ml_backtest to single backtest in example neural networks too.
-
@illustrious-felice Hello.
This is an example of LSTM where 3 features are used for prediction: log(close), log(open), high.
input_dim=3
asset_name_all = ['NAS:AAPL', 'NAS:AMZN', 'NAS:MSFT']You need to modify the
get_modelandget_featuresfunctions to suit your featuresimport xarray as xr # xarray for data manipulation import qnt.data as qndata # functions for loading data import qnt.backtester as qnbt # built-in backtester import qnt.ta as qnta # technical analysis library import numpy as np import logging import pandas as pd import torch from torch import nn, optim asset_name_all = ['NAS:AAPL', 'NAS:AMZN', 'NAS:MSFT'] class LSTM(nn.Module): """ Class to define our LSTM network. """ def __init__(self, input_dim=2, hidden_layers=64): super(LSTM, self).__init__() self.hidden_layers = hidden_layers self.lstm1 = nn.LSTMCell(input_dim, self.hidden_layers) self.lstm2 = nn.LSTMCell(self.hidden_layers, self.hidden_layers) self.linear = nn.Linear(self.hidden_layers, 1) def forward(self, y, future_preds=0): outputs = [] n_samples = y.size(0) h_t = torch.zeros(n_samples, self.hidden_layers, dtype=torch.float32) c_t = torch.zeros(n_samples, self.hidden_layers, dtype=torch.float32) h_t2 = torch.zeros(n_samples, self.hidden_layers, dtype=torch.float32) c_t2 = torch.zeros(n_samples, self.hidden_layers, dtype=torch.float32) for time_step in range(y.size(1)): x_t = y[:, time_step, :] # Ensure x_t is [batch, input_dim] h_t, c_t = self.lstm1(x_t, (h_t, c_t)) h_t2, c_t2 = self.lstm2(h_t, (h_t2, c_t2)) output = self.linear(h_t2) outputs.append(output.unsqueeze(1)) outputs = torch.cat(outputs, dim=1).squeeze(-1) return outputs def get_model(): model = LSTM(input_dim=3) return model def get_features(data): close_price = data.sel(field="close").ffill('time').bfill('time').fillna(1) open_price = data.sel(field="open").ffill('time').bfill('time').fillna(1) high_price = data.sel(field="high").ffill('time').bfill('time').fillna(1) log_close = np.log(close_price) log_open = np.log(open_price) features = xr.concat([log_close, log_open, high_price], "feature") return features def get_target_classes(data): price_current = data.sel(field='close') price_future = qnta.shift(price_current, -1) class_positive = 1 # prices goes up class_negative = 0 # price goes down target_price_up = xr.where(price_future > price_current, class_positive, class_negative) return target_price_up def load_data(period): return qndata.stocks.load_ndx_data(tail=period, assets=asset_name_all) def train_model(data): """ train the LSTM network """ features_all = get_features(data) target_all = get_target_classes(data) models = dict() for asset_name in asset_name_all: model = get_model() # drop missing values: target_cur = target_all.sel(asset=asset_name).dropna('time', 'any') features_cur = features_all.sel(asset=asset_name).dropna('time', 'any') # align features and targets: target_for_learn_df, feature_for_learn_df = xr.align(target_cur, features_cur, join='inner') criterion = nn.MSELoss() # define loss function optimiser = optim.LBFGS(model.parameters(), lr=0.08) # we use an LBFGS solver as optimiser epochs = 1 # how many epochs for i in range(epochs): def closure(): # reevaluates the model and returns the loss (forward pass) optimiser.zero_grad() # input tensor feature_data = feature_for_learn_df.transpose('time', 'feature').values in_ = torch.tensor(feature_data, dtype=torch.float32).unsqueeze(0) # output out = model(in_) # target tensor target = torch.zeros(1, len(target_for_learn_df.values)) target[0, :] = torch.tensor(np.array(target_for_learn_df.values)) # evaluate loss loss = criterion(out, target) loss.backward() return loss optimiser.step(closure) # updates weights models[asset_name] = model return models def predict(models, data): """ predict if price is going up or down and go long depending on it """ weights = xr.zeros_like(data.sel(field='close')) for asset_name in asset_name_all: features_all = get_features(data) features_cur = features_all.sel(asset=asset_name).dropna('time', 'any') if len(features_cur.time) < 1: continue # input tensor feature_data = features_cur.transpose('time', 'feature').values in_ = torch.tensor(feature_data, dtype=torch.float32).unsqueeze(0) # output out = models[asset_name](in_) prediction = out.detach()[0] weights.loc[dict(asset=asset_name, time=features_cur.time.values)] = prediction return weights weights = qnbt.backtest_ml( load_data=load_data, train=train_model, predict=predict, train_period=55, # the data length for training in calendar days retrain_interval=55, # how often we have to retrain models (calendar days) retrain_interval_after_submit=1, # how often retrain models after submission during evaluation (calendar days) predict_each_day=False, # Is it necessary to call prediction for every day during backtesting? # Set it to true if you suspect that get_features is looking forward. competition_type='stocks_nasdaq100', # competition type lookback_period=55, # how many calendar days are needed by the predict function to generate the output start_date='2024-01-01', # backtest start date build_plots=True # do you need the chart? ) -
@vyacheslav_b Thank you so much. I have one more question. When I add stock (NAS:TSLA, NAS:FB,...), I get the following error:
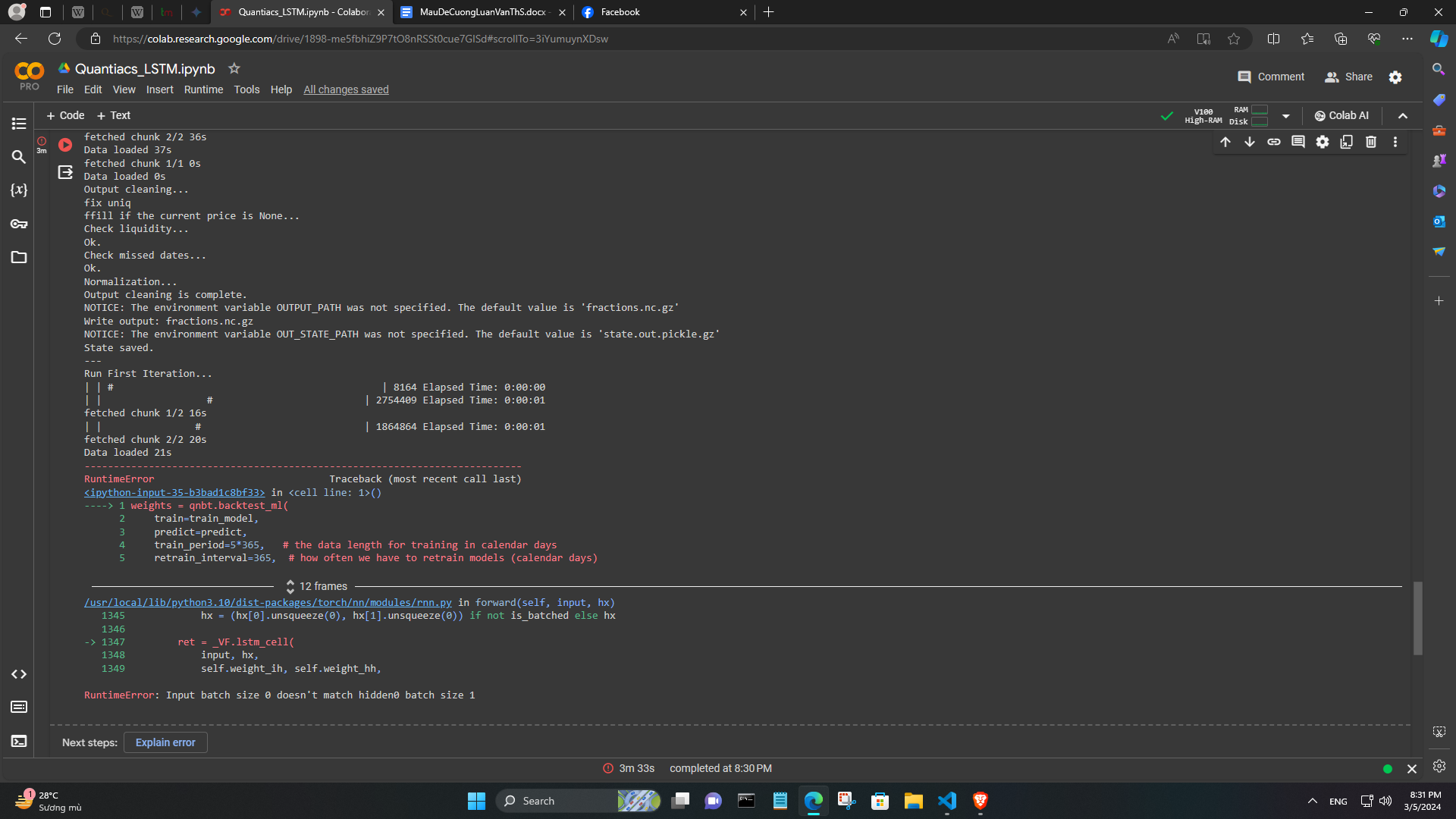
It seems that these tickers are missing data. I tried other codes and found some that could be added like ADBE, GOOGL. I would like to ask why this situation occurs and is there any way to fix it? Thank you very much. -
@illustrious-felice I didn't understand what you mean.
standard functions allow you to fill in gaps with default values
data.sel(field="high").ffill('time').bfill('time').fillna(1) -
@illustrious-felice If I leave the list of stocks as these stocks, the backtest will run normally and I will get the results
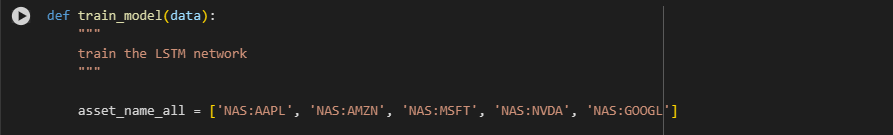
However, if I change to other codes, such as TSLA, FB, META, it will error
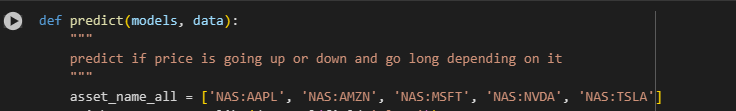
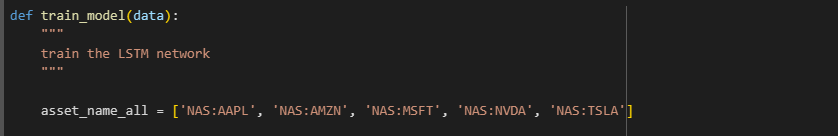
I could only find about 6 or 7 stock codes that didn't have errors -
@illustrious-felice I would like to ask, how can I remove the correlation check each time I run ml_backtest? Thank you so much. Checking correlation is time consuming and I want to eliminate it
-
@illustrious-felice Hello.
Make a copy of your template in your personal account.
In the new version of the qnt library, there is a parameter called check_correlation, which is disabled by default.
I looked at the trading instruments TSLA, FB, META: in 2006, they were not traded on the stock exchange. Try adding one more ticker to the data for these instruments, which was available in 2006.
-
@vyacheslav_b Thank you so much. I would like to ask more, every time I train ml_backtest for LSTM, I get a different sharpe result (sometimes the sharpness is 1.2, 1.1, 0.9,...) Why is there the following sharpness inconsistency? Every time you train like that? We wish to be answered. Thank you.
-
Incorporating seed initialization into your PyTorch code ensures reproducibility by making the random number generation predictable. This involves setting seeds for the PyTorch engine, NumPy, and the Python random module if you're using it. Below, I'll show you how to integrate seed initialization into your existing code. Remember, while this can make your experiments more reproducible, it does not guarantee identical results across different hardware or PyTorch versions due to the inherent nondeterminism in some GPU operations.
import xarray as xr # xarray for data manipulation import qnt.data as qndata # functions for loading data import qnt.backtester as qnbt # built-in backtester import qnt.ta as qnta # technical analysis library import numpy as np import pandas as pd import torch from torch import nn, optim import random # Seed initialization function def set_seed(seed_value=42): """Set seed for reproducibility.""" random.seed(seed_value) np.random.seed(seed_value) torch.manual_seed(seed_value) torch.cuda.manual_seed(seed_value) torch.cuda.manual_seed_all(seed_value) # if you are using multi-GPU. torch.backends.cudnn.deterministic = True torch.backends.cudnn.benchmark = False # Set the seed for reproducibility set_seed(42) asset_name_all = ['NAS:AAPL', 'NAS:AMZN', 'NAS:MSFT'] class LSTM(nn.Module): """ Class to define our LSTM network. """ def __init__(self, input_dim=3, hidden_layers=64): super(LSTM, self).__init__() self.hidden_layers = hidden_layers self.lstm1 = nn.LSTMCell(input_dim, self.hidden_layers) self.lstm2 = nn.LSTMCell(self.hidden_layers, self.hidden_layers) self.linear = nn.Linear(self.hidden_layers, 1) def forward(self, y, future_preds=0): outputs = [] n_samples = y.size(0) h_t = torch.zeros(n_samples, self.hidden_layers, dtype=torch.float32) c_t = torch.zeros(n_samples, self.hidden_layers, dtype=torch.float32) h_t2 = torch.zeros(n_samples, self.hidden_layers, dtype=torch.float32) c_t2 = torch.zeros(n_samples, self.hidden_layers, dtype=torch.float32) for time_step in range(y.size(1)): x_t = y[:, time_step, :] # Ensure x_t is [batch, input_dim] h_t, c_t = self.lstm1(x_t, (h_t, c_t)) h_t2, c_t2 = self.lstm2(h_t, (h_t2, c_t2)) output = self.linear(h_t2) outputs.append(output.unsqueeze(1)) outputs = torch.cat(outputs, dim=1).squeeze(-1) return outputs def get_model(): model = LSTM(input_dim=3) return model def get_features(data): close_price = data.sel(field="close").ffill('time').bfill('time').fillna(1) open_price = data.sel(field="open").ffill('time').bfill('time').fillna(1) high_price = data.sel(field="high").ffill('time').bfill('time').fillna(1) log_close = np.log(close_price) log_open = np.log(open_price) features = xr.concat([log_close, log_open, high_price], "feature") return features def get_target_classes(data): price_current = data.sel(field='close') price_future = qnta.shift(price_current, -1) class_positive = 1 # prices goes up class_negative = 0 # price goes down target_price_up = xr.where(price_future > price_current, class_positive, class_negative) return target_price_up def load_data(period): return qndata.stocks.load_ndx_data(tail=period, assets=asset_name_all) def train_model(data): features_all = get_features(data) target_all = get_target_classes(data) models = dict() for asset_name in asset_name_all: model = get_model() target_cur = target_all.sel(asset=asset_name).dropna('time', 'any') features_cur = features_all.sel(asset=asset_name).dropna('time', 'any') target_for_learn_df, feature_for_learn_df = xr.align(target_cur, features_cur, join='inner') criterion = nn.MSELoss() optimiser = optim.LBFGS(model.parameters(), lr=0.08) epochs = 1 for i in range(epochs): def closure(): optimiser.zero_grad() feature_data = feature_for_learn_df.transpose('time', 'feature').values in_ = torch.tensor(feature_data, dtype=torch.float32).unsqueeze(0) out = model(in_) target = torch.zeros(1, len(target_for_learn_df.values)) target[0, :] = torch.tensor(np.array(target_for_learn_df.values)) loss = criterion(out, target) loss.backward() return loss optimiser.step(closure) models[asset_name] = model return models def predict(models, data): weights = xr.zeros_like(data.sel(field='close')) for asset_name in asset_name_all: features_all = get_features(data) features_cur = features_all.sel(asset=asset_name).dropna('time', 'any') if len(features_cur.time) < 1: continue feature_data = features_cur.transpose('time', 'feature').values in_ = torch.tensor(feature_data, dtype=torch.float32).unsqueeze(0) out = models[asset_name](in_) prediction = out.detach()[0] weights.loc[dict(asset=asset_name, time=features_cur.time.values)] = prediction return weights weights = qnbt.backtest_ml( load_data=load_data, train=train_model, predict=predict, train_period=55, retrain_interval=55, retrain_interval_after_submit=1, predict_each_day=False, competition_type='stocks_nasdaq100', lookback_period=55, start_date='2024-01-01', build_plots=True )I think I won't be available next week. If you have any more questions, don’t expect an answer from me next week.